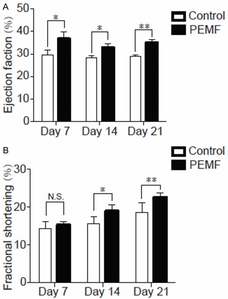
Extracorporeal pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) has been shown the ability to improve regeneration in various ischemic episodes. Here, we examined whether PEMF therapy facilitate cardiac recovery in rat myocardial infarction (MI), and the cellular/molecular mechanisms underlying PEMF-related therapy was further investigated. The MI rats were exposed to active PEMF for 4 cycles per day (8 minutes/cycle, 30 ± 3 Hz, 5 mT) after MI induction. The data demonstrated that PEMF treatment significantly inhibited cardiac apoptosis and improved cardiac systolic function. Moreover, PEMF treatment increased capillary density, the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxic inducible factor-1α in infarct border zone. Furthermore, the number and function of circulating endothelial progenitor cells were advanced in PEMF treating rats. In vitro, PEMF induced the degree of human umbilical venous endothelial cells tubulization and increased soluble pro-angiogenic factor secretion (VEGF and nitric oxide). In conclusion, PEMF therapy preserves cardiac systolic function, inhibits apoptosis and trigger postnatal neovascularization in ischemic myocardium.
Jan 15, 2024 1:22 pm